Dental X-Rays: Why They’re Important for Diagnosis
Introduction
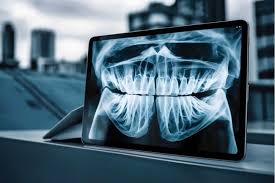
Dental X-rays are one of the most powerful diagnostic tools in modern dentistry. They allow dentists to detect problems that aren’t visible to the naked eye — from tiny cavities between teeth to bone loss beneath the gums. Without X-rays, many dental conditions could go unnoticed until they cause pain or serious complications. Understanding how dental X-rays work and why they’re important for diagnosis can help you take better care of your oral health.
What Are Dental X-Rays?
Dental X-rays (radiographs) are images of your teeth, gums, and jawbone taken using low levels of radiation. They help dentists identify issues such as decay, infection, bone loss, or developmental abnormalities that can’t be seen during a regular dental exam.
Modern dental clinics use digital X-rays, which produce instant results and expose you to significantly less radiation compared to traditional film-based systems.
Why Dental X-Rays Are Important
1. Early Detection of Dental Problems
X-rays help detect issues before they become visible or painful, enabling early treatment and preventing complications.
They can identify:
- Small cavities between teeth
- Early stages of tooth decay under fillings
- Bone loss caused by gum disease
- Infections near the tooth root
- Cysts or tumors in the jaw
Early detection through dental X-rays often means less invasive, less costly treatments.
2. Monitoring Tooth and Jaw Development
For children and teenagers, dental X-rays are crucial in tracking tooth growth and jaw alignment. They help dentists monitor the eruption of permanent teeth, detect extra or missing teeth, and guide orthodontic treatments like braces.
In adults, X-rays help monitor bone density, detect wisdom teeth growth, and check implant placement.
3. Diagnosing Periodontal (Gum) Disease
Gum disease affects not only the soft tissues but also the underlying bone structure. Dental X-rays reveal the extent of bone loss around teeth — a key factor in diagnosing and managing periodontitis.
With this information, dentists can develop personalized treatment plans to stop the progression of gum disease.
4. Identifying Infections and Abscesses
X-rays can detect infections at the tooth’s root or in the surrounding bone before symptoms like swelling or pain occur. These infections, called abscesses, require prompt treatment to prevent tooth loss or the spread of infection to other parts of the body.
5. Evaluating Dental Restorations and Procedures
Dental X-rays help ensure that treatments such as crowns, fillings, root canals, and implants are successful. They allow dentists to check the fit, placement, and integrity of restorations and to detect potential complications like hidden decay beneath them.
Types of Dental X-Rays
Different X-rays provide specific views of your mouth. Here are the main types used in dentistry:
| Type of X-Ray | Area Captured | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Bitewing | Upper and lower back teeth | Detect cavities and bone loss |
| Periapical | Entire tooth (root to crown) | Identify abscesses or cysts |
| Panoramic | Full mouth and jaw | Evaluate wisdom teeth, bone structure, and sinus issues |
| Occlusal | Floor or roof of the mouth | Detect extra or unerupted teeth |
| Cephalometric | Side profile of head | Used in orthodontic planning |
Each X-ray type plays a vital role depending on the patient’s age, dental history, and symptoms.
Are Dental X-Rays Safe?
Yes, dental X-rays are extremely safe when performed correctly. The amount of radiation exposure is minimal — roughly equivalent to what you naturally receive from the environment in a single day.
Modern safety measures include:
- Use of digital X-rays (80–90% less radiation than traditional film)
- Lead aprons and thyroid collars for protection
- Strict adherence to dental safety protocols
For pregnant patients, dentists usually postpone X-rays unless absolutely necessary to avoid any unnecessary exposure.
How Often Should You Get Dental X-Rays?
The frequency of X-rays depends on your dental health, age, and risk factors.
General guidelines:
- Children: Every 6–12 months to monitor tooth development
- Adults with good oral health: Every 1–2 years
- Patients with gum disease or high cavity risk: More frequently as advised by the dentist
Regular dental visits help your dentist determine the right schedule for your needs.
Benefits of Dental X-Rays
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Early diagnosis | Detects decay and disease before symptoms appear |
| Prevention | Helps stop problems from worsening |
| Treatment planning | Guides dental procedures like implants or orthodontics |
| Cost-effective care | Reduces need for expensive treatments |
| Comprehensive monitoring | Tracks changes in oral health over time |
These advantages make X-rays one of the most essential tools in preventive dentistry.
Dental X-Rays in Modern Dentistry
Modern dental clinics, like digital diagnostic centers, use high-resolution imaging technology that provides instant, detailed visuals. These images are stored electronically, allowing dentists to compare your results over time and identify even subtle changes in oral health.
This shift from traditional film to digital radiography not only improves accuracy but also reduces radiation exposure, making diagnostics faster, safer, and more efficient.
Conclusion
Dental X-rays are an indispensable part of oral health care. They provide valuable insights that visual exams simply can’t reveal, helping detect problems early, monitor growth, and guide treatments effectively. Regular X-rays — combined with professional checkups and proper oral hygiene — ensure that your teeth and gums stay healthy for life. If you haven’t had X-rays in a while, talk to your dentist about scheduling one at your next appointment.
FAQs
Q1. Are dental X-rays painful?
No, dental X-rays are completely painless. You might experience slight discomfort from holding the film or sensor in your mouth, but it only lasts a few seconds.
Q2. How much radiation do dental X-rays expose you to?
A single digital dental X-ray exposes you to about 0.005 millisieverts (mSv) of radiation — less than what you’re exposed to naturally in a day.
Q3. Can pregnant women get dental X-rays?
X-rays are usually postponed during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary. If needed, protective measures like lead aprons are used to shield the abdomen.
Q4. Why are X-rays needed if my teeth look fine?
Many dental issues, like cavities between teeth or bone loss, develop beneath the surface. X-rays reveal hidden problems before they become painful or costly.
Q5. How long do dental X-rays take?
Most dental X-rays take only 5–10 minutes and provide instant results with digital imaging systems.











Post Comment